|
Characteristics
of the Japanese Digital
BS Broadcasting System
Present
condition of digital broadcasting
in Japan
Digital satellite
television broadcasting
began for the first time
in the United States in
1994, followed by Europe
and Asia around 1996.
Japan also started digital
CS broadcasting using
communication satellites
(CS) in 1996. These satellite
digital broadcasts provide
mainly multi-channel standard
definition TV services.
As for the technological
development of digital
satellite broadcasting
using broadcast satellites
(BS), the NHK Science
& Technical Research Laboratories
initiated the research
for ISDB (Integrated Services
Digital Broadcasting)
around 1982. Thorough
examinations were carried
out from the perspective
of efficient use of the
limited frequency resources
allotted to broadcasting.
In the process, a new
concept for broadcasting
services, not simply replacing
conventional analog services
with the digital format,
has been developed that
makes the best use of
the merits of digitization;
the flexibility of service
arrangements inherent
to digital signals, the
expansion capability for
new services in the future,
and the community of diverse
media.
A report concerning digital
BS broadcasting, which
is scheduled to start
in the year 2000, has
been issued by the Telecommunications
Technology Council, and
technical systems such
as transmission/multiplexing
systems and video/sound
encoding formats finalized.
The ARIB (Association
of Radio Industries and
Businesses), a nongovernment
standardization organization,
has set the SI (Service
Information), and CAS
(Conditional Access System)standards
for data broadcasting
systems.
Digital
satellite broadcasting
system
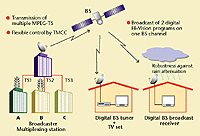 |
| Figure
1: Digital BS broadcasting
image |
Our image of the shape of
digital BS broadcasting
with these characteristics
is shown in Figure 1.
The chief characteristics
of digital BS system are
as follows;
(1) Large capacity transmission
Trellis Coded (TC) 8PSK
modulation has been adopted,
which is capable of a maximum
52Mbps capacity on a single
34.5MHz broadband BS broadcast
channel. This arrangement
enables the simultaneous
broadcast of 2 HDTV and
four sound broadcasts, in
addition to multiple data
broadcasting on only one
BS channel.
(2) Hierarchical transmission
service
In addition to the selection
capability of the transmission
format (modulation or error
correction) corresponding
to the contents of the broadcast
service, multiple transmission
schemes can be used simultaneously
by one channel.
Satellite broadcasting has
a tendency to be affected
by heavy rain or other harsh
weather conditions, resulting
in a sudden service interruption.
Digital broadcasting will
be able to provide hierarchical
transmission services with
simultaneous broadcasting
of both a program and a
transmission system which
makes broadcast interruption
unlikely even with weaker
signals. These hierarchical
transmission services will
make possible HDTV broadcasts
with high-definition images
during usual weather conditions,
and basic broadcasting consisting
of still picture/reduced
video signals in heavy rain,
allowing continuous viewing
of a program.
(3) Multiplexing TSs
on one channel
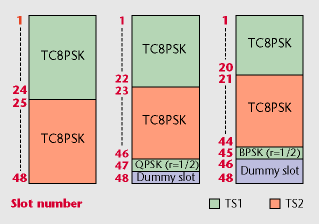 |
| Figure
2: Example of slot
transmission scheme
allocation in one
channel |
In digital BS broadcasting,
one channel is time-divided
into 48 slots. One slot's
transmission capacity is
1.08 Mbps. MPEG TS (Transport
Stream) transmission can
be carried out by utilizing
several of these slots.
Each digital BS channel
is capable of simultaneous
broadcasting that combines
four different transmission
schemes. An example allocation
of TSs and transmission
schemes into slots is shown
in Figure 2.
Each digital BS channel
can, therefore, multiplex
multiple TSs. Every digital
broadcaster will be allotted
individual TSs, and optional
service arrangements within
each TS can be made by each
broadcaster.
To enable flexibility regarding
the adjustment of information
amounts and the combination
of transmission schemes
on each TS, TMCC (Transmission
& Multiplexing Configuration
Control) signals are also
included.
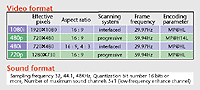 |
| Table
1: Video and sound
formats |
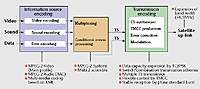 |
| Figure
3: Digital BS broadcasting
system structure and
each sector's technical
characteristics |
(4) International coordination
encoding system
In consideration of
international coordination,
we adopted MPEG-2 Video
for the video encoding system,
and MPEG-2 Audio ACC for
the sound encoding system,
both having a high-compression
efficiency and capable of
high-quality sound broadcasting.
Multiplexing also uses the
MPEG-2 format. Data broadcasting
has a multimedia encoding
system based on the W3C
standard XML. These features
are designed to facilitate
international digital program
exchange.
Structural and technological
details of the digital satellite
broadcasting system with
these characteristics are
shown in Figure 3. Video
and sound formats using
digital BS broadcasting
are shown in Table 1. |

