Digital Data Receiver
(Japanese patent No 2912323, US patent pending)
BS digital broadcasting has a high channel capacity, 52 Mbps per carrier,
for transmission of two HDTV and variety of data programs in one carrier.
One satellite transponder, which is assigned to one carrier, is usually
shared by two or more broadcasters. Thus, in contrast with a conventional
broadcasting system, the BS digital broadcasting system can simultaneously
utilize more than one modulation scheme so as to meet to the transmission
requirements of each broadcaster; a high C/N modulation scheme, such
as TC8PSK, is employed to maximize channel capacity and a low C/N one,
such as QPSK or BPSK, ensures reliable transmission during periods of
heavy rainfall. A broadcaster could also choose to use two modulation
schemes; simultaneous use of TC8PSK and QPSK realizes a hierarchical
transmission scheme that extends the broadcaster's service availability.
Given some combination of modulation schemes, a packet that is modulated
by a high C/N modulation scheme deteriorates quicker than one modulated
by a low C/N scheme when the received C/N becomes degraded. When received
C/N decreases due to heavy rain, a deteriorated packet transmitted by
TC8PSK might become mislabeled with the packet ID of another packet
group transmitted by QPSK or BPSK. This results in the deteriorated
packet affecting the decoding process that is used for getting information
via QPSK or BPSK.
In this invention, a receiver is composed of any combination of demodulator
and bit error correction and threshold judgment circuits in order to
get packet data from the multiplex transmission signal. The received
conditions of the respective transmission schemes are detected by the
error correction and threshold judgment circuits. When a transmission
scheme is judged to be unusable due to bit errors, the relevant packet
is replaced by a null packet that does not affect correctly transmitted
packets in the decoder. Under a low C/N condition, data transmitted
by a low C/N transmission scheme can be effectively prevented from being
influenced by data transmitted by a high C/N transmitted scheme.
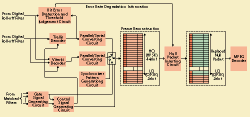
The figure illustrates an embodiment of the digital demodulator for
the time division multiplexed signal in which the TMCC (Transmission
and Multiplexing Configuration Control) signal that carries the configuration
of multiplexing and modulation scheme of each packet is multiplexed.
The demodulation process is controlled by the TMCC. The transmission
conditions of respective transmission schemes are detected in the bit
error detection and threshold judgment circuits. When the receiving
condition is judged to be unusable because of a high bit error rate,
a control signal that has information on error rate degradation is used
to replace the relevant packet with a null packet or any other signal
that does not affect correctly transmitted packets at the null packet
inserting circuit.
 |
| Figure: Block diagram of digital receiver |
|

