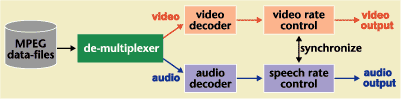
|
| High-Performance
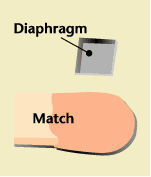
Ultra-small IC Microphone
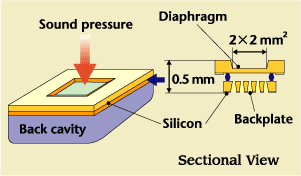
STRL has developed a condenser-type IC microphone with superb characteristics. In contrast with conventional microphones, which have many metal and resinous parts, the IC microphone is produced from silicon wafers through a continuous micro-machining process that is based on LSI manufacturing technology. This allows us to consistently fabricate a high-performance ultra-small microphone at a low-price. The microphone's design also has a large degree of freedom because of the unique manufacturing process of the condenser, which uses a multi-layered substrate whose thickness can be controlled. This makes possible production of microphones having optimum shapes and characteristics for a wide range of applications, from high-performance professional-use microphones for interviews and recording music, to microphones for consumer appliances such as portable terminals. Note: Tohoku University cooperated in the development
of the technologies used to make the new microphone. Their contributions
include anisotropic etching, a technology used to carve patterns only
in the direction normal to the surface of the substrate.
|
|
|