|
| The Future Evolution of Digital Broadcasting |  |
Kazuo FUKUI, Director, Advanced Audio & Video Coding |
| The future evolution of digital broadcasting has two aspects.
One is the evolution induced by digital broadcasting expansion, and the
other the evolution linked to various pieces of peripheral equipment and
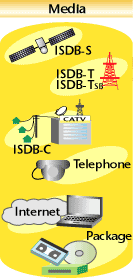
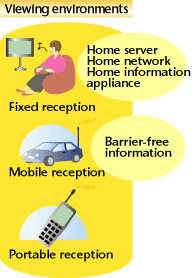
the communications media. The technical standards for digital broadcasting in Japan are together called the ISDB Family. This consists of ISDB-S (Satellite) for satellite broadcasting, ISDB-C (Cable) for cable TV networks, ISDB-T (Terrestrial) and ISDB-TSB (Terrestrial Sound Broadcasting) for terrestrial broadcasting. Implementation of the ISDB Family started when the digital BS broadcasting service commenced in 2000. This was followed by the advancing digitalization of cable TV networks. Digital broadcasting via the terrestrial broadcast network is scheduled to start in three major metropolitan areas in 2003. ISDB-T and ISDB-TSB have adopted technologies assuming mobile and portable reception, which will make digital broadcasting services available during any daily activity. Along with the progress of the storage technology, the TV-anytime service will become reality in the near future. The development of a home-server and new services that are intended for use with the new functions of the home-server is going on at the STRL. A home-server will also work as a gateway that connects various networks, such as those of broadcasting, communications, and cable TV, to a home network. Even the microwave oven will be connected to a digital receiver over a home network, and follow the cooking instructions provided via data broadcasting. Another example is "ch@Net", which has been developed as a new Internet service to link broadcasting to the Internet. By using a remote controller, similar to that used for the conventional TV set, the "ch@NET" service provides the instant display of a program's web page on a PC, while the program is watched on the TV. New online service experiments are also being carried out by broadcasters to make previously broadcast news contents available on the Internet. Studies are also underway on information barrier-free broadcasting. The studies will maintain the place of broadcasting as the most familiar information medium usable to anybody. Based on these studies, people of advanced age or with physical difficulties will be able to access information with ease. In this way, broadcasting will be more enjoyable for everyone. Broadcasting services had evolved independently from other information services in the past. Now, however, new aspects have emerged in the relationship between communication services and the various information appliances, due to digitalization. As a result, broadcasting is becoming one of the universal information media, and will continue as major information medium that surpasses the conventional frame work of the past. |
|