Personalized EPG Using User
Preference Metadata
From July through December 2000, Mr. Akkaya of the Turkish-Radio
Television Corporation (TRT) conducted research on metadata in digital
broadcasting at NHK Science and Technical Research Laboratories
as an invited researcher of the Asia Broadcasting Union (ABU). His
research activities, which focused on "Personalized EPG using user
preference metadata," were aimed at developing an EPG (Electronic
Program Guide) system that automatically selects and shows programs
reflecting the user's preferences, on the basis of the TV Anytime
system and other standardizations in metadata. In this article,
the system model and implementations of the personalized EPG are
described.
|
What is metadata?
Metadata is generally defined as "Data about data". It is a term
used in a very wide area, including computer science and telecommunications.
In broadcasting, metadata is descriptive information of contents,
and is transmitted along with the contents. It is produced and utilized
by broadcasters in the process of program production, exchange,
transmission, and archiving. The EPG provided for digital broadcasting
can be considered as one form of metadata. The EPG metadata can
be utilized by users to search, navigate, and manage content. Moreover,
user preferences, such as a preferred genre, a favorite movie actor,
frequently selected channel, and so on, are considered as kinds
of metadata.
Metadata standardization
a. Organization
SMPTE (Society of Motion Pictures and Television Engineering) is
developing a coding and transmission system for metadata, and making
definitions for metadata dictionaries. MPEG-7 (Moving Pictures Experts
Group) is also working on metadata to describe multimedia contents.
It has been decided to adopt XML (Extensible Markup Language) Schema
Language as a framework to express and transmit metadata. EBU (European
Broadcast Union) is focusing on metadata applications and the standardization
of data exchange and archiving through its sub-groups, P/META (Project
of Metadata) and FTA (Future Television Archives). ARIB (Association
of Radio Industries Business) in Japan has established a working
group for broadcasting systems based on Home Servers. Metadata systems
for digital storage in consumer platforms have been studied.
b. TV Anytime Forum
The TV Anytime Forum standardizes multimedia services based on digital
storage in consumer platforms, combining the immediacy of television
with the flexibility of the Internet. A simple system model for
a TV Anytime system is described in Figure 1. Users will be able
to explore and acquire TV contents from a variety of sources, including
traditional broadcast and new on-line interactive services, at anytime.
In order to realize TV Anytime concepts, the forum has been standardizing
technologies that include metadata. The TV Anytime metadata system
allows the consumer to find, navigate and manage content from a
variety of internal and external sources including, for example,
broadcasting, Internet and local storage. Also, it should be able
to handle information concerning rights management and protection,
financial transactions, and security.
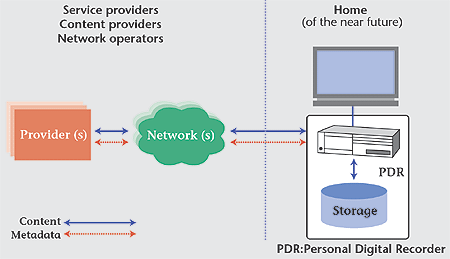 |
| Figure 1: TV Anytime, simple system model |
Personalized EPG
As the number of channels and programs increases, the users will
need to be provided with their own EPG for selecting programs
according to their individual preferences and profiles. This process
is a kind of filtering. The users are presented with an EPG containing
a list of content based on their own preferences. After the user
has selected a desired piece of content with its description on
the EPG, search and navigation processes are initiated through
content referencing mechanisms. After capturing, the content is
recorded whenever and on whatever channel regardless of any subsequent
changes in the program scheduling.
System model for personalized EPG by
user preference metadata
Figure 2 shows the system description for the personal EPG. In
this system, metadata is used not only on the content provider's
side but also on the user's side (in the PDR). The user enters
his/her preferences as metadata to make the Personalized EPG,
which is formed depending on the user's own interests.
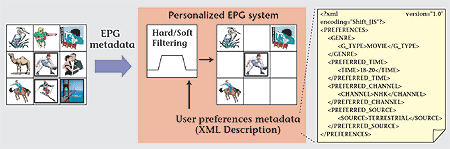 |
| Figure 2: System model personalized EPG
by user preference metadata |
The following concepts have been adopted to realize the personalized
EPG:
a. User preference and profile
The user preference and profile
will be produced in the PDR to personalize the EPG. This kind of
metadata is produced either manually with some user interfaces or
automatically through the use of agents. These user data are described
as XML documents according to the standards. The data in the PDR
is also used by other agencies (like the service or content provider)
to provide data that is convenient for the user.
b. "Hierarchical preference" and "Hard/soft filtering"
With the personalized EPG using user preference metadata, if a user
is interested in golf, for example, events, advertisements and news
related to golf will be "filtered" through the PDR to the screen.
The user will not be bored with countless other news and information
items, advertisements, etc., outside the range of his/her interests.
But this has to be carried out within some kind of a ranking system;
for example, one user may want to have only the programs that he
has indicated (hard filtering), whereas another might prefer a range
of similar programs to his/her stated preferences (soft filtering).
So, in the EPG system, a "hierarchical preference that allows multiple
choice in the ranking and hard/soft filtering properties have to
be provided.
c. Personalization in the family
A new "Family PDR" concept
has been adopted for the EPG system. Considering the multiple user
interests in a typical family, a PDR has to be designed to allow
each member in the family to have a separate personalized interface
(e.g. the interests of the father and daughter can be totally different.).
Everybody uses a part of the PDR storage under their own management,
arranging their own storage and user profiles.
Implementations
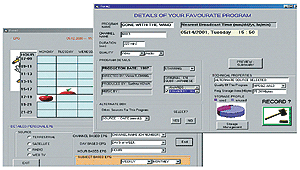 |
| Figure 3: Personalized EPG User Interface
Application |
A personalized EPG model has been implemented.
In the user interface for the registration of preference, the user
simply enters his/her preferences such as genre, time of day for
watching, preferred channel, preferred source (Terrestrial, Satellite,
Internet, etc.). As this system is provided with the "Soft Filtering"
architecture, it does not have strict parameters for multiple selection
and ranking among the preferences. The system extracts these preferences
and forms an XML document file, which is used to present the personalized
EPG to the user. Figure 3 shows a developed Personalized EPG user
the interface application. As the system adopts the XML schema language
to describe user preferences, it realizes flexibility, extensibility,
and interoperability with other systems. The user-friendly interface
and simple input features including point and click record selection
from the EPG.
Summary
The personalized EPG using user preference metadata has been developed.
It realizes a navigation system that selects suitable programs from
among a huge number of channels and programs according to user preferences.
The hard/soft filtering concept has been newly developed for the
EPG system, which selects programs according to hierarchical user
preferences. The EPG system has been designed to provide a personalized
interface to each user under a multi-user environment in the family.
The personalized EPG model has been implemented with the XML Schema
Language adopted to describe metadata on both programs and user
preferences, to make the system both flexible and extensible.
(Murat Koray Akkaya, Turkish Radio and Television (TRT) & Keigo
MAJIMA, Recording Technology & Mechanical Engineering)
References
| [1] |
The TV Anytime Forum : "Call for Contributions On": Metadata,
Content Referencing, and Rights Management, TV014r3 (Dec.
1999) |
|
|

